


Motor works in the same way as Push, but applies rotational torque to the affected particles or objects rather than a directional force. Note that, when applied to particles, both the position and orientation of the Motor icon affects the particles, which swirl around the Motor icon. When used in dynamics, the relative position of the icon to the affected object has no affect, but the orientation of the icon does.

The U.I. components for Motor are identical with those of Push, with the following exceptions:
On Time/Off Time: The times that the space warp begins its effect and ends its effect. Note that, because Push moves the objects to which it’s applied, those objects will move over time, although there are no keyframes created.
Basic Torque: The amount of force exerted by the space warp.
N-m/Lb-ft/Lb-in: These three options specify the unit of measure for the Basic Torque setting, using common world measurements of torque. N-m stands for Newton-meters, Lb-ft is pounds-feet, and Lb-in is pounds-inch.
Feedback On: When this is checked, the force lessons, depending on how near the affected objects get to the specified Target Speed value (described below). When this is unchecked, the force remains constant, regardless of the speed of the affected objects.
Reversible: When checked, if the objects speed exceeds the Target Speed the force is reversed.
Target Revs: This is only used when Feedback is checked. It specifies the maximum revolutions before the Feedback takes effect. Speed is specified in units traveled per frame.
RPH/RPM/RPS: Specifies the units of measure for the Target RevsRevolutions-per-Hour, Minute, or Second.
Gain %: Specifies how quickly the force adjusts to the approach to target speed. If this is set to 100 percent, the correction is immediate. If it’s lower, a slower and “looser” response occurs. Note that this spinner can be set above 100 percent, This will often result in overcorrection, but Gains greater than 100 percent are sometimes necessary to overcome damping from other system settings, such as IK damping, and so on.
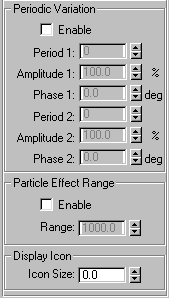
Provides settings that introduce variations into the force by affecting the Basic Force value randomly. You can set two waveforms to produce more of a noise effect.
Enable : Check this to turn on the variations.
Period 1 : The time over which the noise variation makes a full cycle. For example, a setting of 20 means one cycle per 20 frames.
Amplitude 1 % : The strength of the variation. This uses the same types of units as the Basic Force spinner.
Phase 1 : Offsets the variation pattern.
Period 2 : The next two spinners provide an additional variation pattern to increase the noise.
Amplitude 2 %
Phase 2
Lets you restrict the Push effect to a specific range. Note that this only affects particles systems; it has no effect on Dynamics.
Enable: Check this to limit the range of the effect to a sphere, displayed as a tri-hooped sphere. The effect falls off increasingly as the particles near the boundary of the sphere..
Range: Specifies the radius of the range of the effect, in units.
Icon Size (spinner): Sets the size of the Push icon. This is for display purposes only, and does not alter the Push effect.
The Motor appears as a box-shaped icon with an arrow indicating the direction of the tork..