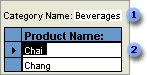
A subform is a form that is inserted in another form. The primary form is called the main form, and the form within the form is called the subform. A form/subform combination is often referred to as a hierarchical form, a master/detail form, or a parent/child form.
Subforms are especially effective when you want to show data from tables or queries with a one-to-many relationship. For example, you could create a form with a subform to show data from a Categories table and a Products table. The data in the Categories table is the "one" side of the relationship. The data in the Products table is the "many" side of the relationship ù each category can have more than one product.

 The main form shows data from the "one" side of the relationship.
The main form shows data from the "one" side of the relationship.
 The subform shows data from the "many" side of the relationship.
The subform shows data from the "many" side of the relationship.
The main form and subform in this type of form are linked so that the subform displays only records that are related to the current record in the main form. For example, when the main form displays the Beverages category, the subform displays only the products in the Beverages category.
 Displaying a subform in a form
Displaying a subform in a form
When you create a subform, you can design it to be displayed in Datasheet view, Form view, PivotTable view, or PivotChart view. You can also set the default view of the subform, and disable one or more views. You can switch the view of a subform when the main form is displayed in Form view.
Subforms are not displayed when a main form is opened in PivotTable or PivotChart view.
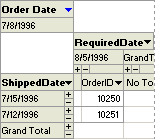
 A subform displayed in Datasheet view
A subform displayed in Datasheet view
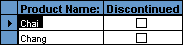
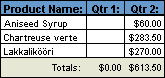
 A subform displayed as a simple continuous form in Form view
A subform displayed as a simple continuous form in Form view
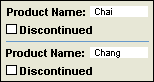
 A subform displayed as a continuous form in Form view
A subform displayed as a continuous form in Form view
You can make a form displayed in Form view look like a datasheet, but since it's displayed in Form view, it can display a form header and footer.
 A subform displayed in PivotTable view
A subform displayed in PivotTable view
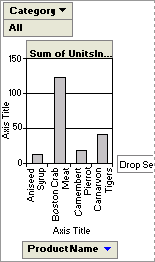
 A subform displayed in PivotChart view
A subform displayed in PivotChart view
 Synchronizing a form and a subform
Synchronizing a form and a subform
When you create a form and subform based on tables that have a one-to-many relationship, the main form shows the "one" side of the relationship and the subform shows the "many" side of the relationship. The main form is synchronized with the subform so that the subform shows only records related to the record in the main form.
If you use a wizard to create a subform, or if you drag a form, table, or query from the Database window to another form to create a subform, Microsoft Access automatically synchronizes the main form with the subform if one of the following conditions is met:
 Nesting levels
Nesting levels
A main form can have any number of subforms if you place each subform on the main form. You can also nest up to seven levels of subforms. This means you can have a subform within a main form, and you can have another subform within that subform, and so on. For example, you could have a main form that displays customers, a subform that displays orders, and another subform that displays order details. However, a form will not display subforms in PivotTable or PivotChart view.
 Entering data using a form and subform
Entering data using a form and subform
When you use a form with a subform to enter new records, Microsoft Access saves the current record in the main form when you enter data in the subform. This ensures that the records in the "many" table will have a record in the "one" table to relate to. It also automatically saves each record as you add it to the subform.