 appears just below your pasted selection after you paste text. When you click the button, a list appears that lets you decide how the information is pasted into your document.
appears just below your pasted selection after you paste text. When you click the button, a list appears that lets you decide how the information is pasted into your document.When you paste information into Microsoft Word, you can decide how it is formatted in most cases.
The Paste Options button  appears just below your pasted selection after you paste text. When you click the button, a list appears that lets you decide how the information is pasted into your document.
appears just below your pasted selection after you paste text. When you click the button, a list appears that lets you decide how the information is pasted into your document.
The available options depend on the type of content you are pasting, the program you are pasting from, and the format of the text where you are pasting.
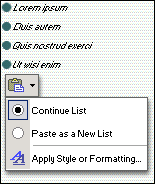
For example, if you are pasting list items near a list, you can decide whether the pasted text is included in the list or is pasted as a new list. If you are pasting into a paragraph, you can decide whether the text keeps its original formatting or is formatted like surrounding text.
If you are pasting data from Microsoft Excel, you can specify whether or not you want to link the data, and how you want to format the data.
 Pasting information to or from other programs
Pasting information to or from other programs
Information you cut or copy to another program is pasted, if possible, in a format that the program can edit.
For example, data from Microsoft Excel worksheets and records from Microsoft Access are pasted by default into Word as Word tables, complete with column widths and font formatting. Text separated by tab characters from Word is pasted into Excel in rows and columns of cells.
If a program can't edit the information, it inserts it as an embedded object. You can use the source program to edit embedded objects. If the information can't be inserted, it is pasted as a static picture that cannot be edited.
 The default format of pasted text
The default format of pasted text
The default format of pasted text can be affected by whether or not you include a paragraph mark or section break in your selection, although you can change many formatting attributes as you paste with the Paste Options button  .
.
Notes
To view paragraph marks and section breaks on the screen, click Show/Hide 
 on the Standard toolbar.
on the Standard toolbar.