www.marco
cantu.com
Copyright 1997
Marco Cantù
Delphi Developers' Handbook
Chapter 15: Other Delphi Extensions
Copyright Marco Cantu' 1997Handling Delphi Notifications
Our first VCS displayed the project information form we previously used in the Project Wizard, with only a couple of minor changes. We updated this project window each time the user changed the project, simply because the VCS interface notifies us of a project change without telling us what happened.
To make the program more powerfulùand to introduce another Delphi featureùletÆs explore how we can handle Delphi file notifications via an add-in notifier object. (This add-in notifier interface is available in any situation where you have access to the global ToolServices object. Therefore, you can respond to Delphi notifications in a VCS, a wizard, a component or property editor, and so on.)
To install an add-in notifier object in Delphi you use the following ToolServices method:
function AddNotifier(AddInNotifier: TIAddInNotifier): Boolean; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
The TIAddInNotifier class (the type of the first parameter) is quite simple, since it declares only one method you should override:
type
TIAddInNotifier = class(TInterface)
public
procedure FileNotification(NotifyCode: TFileNotification;
const FileName: string; var Cancel: Boolean); virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
procedure EventNotification(NotifyCode: TEventNotification;
var Cancel: Boolean); virtual; stdcall; abstract;
end;
Whenever a file operation occurs, Delphi will call the FileNotification method. In the body of this method, you can access the filename and a notification code, as well as a Boolean reference parameter that you can use to cancel the operation causing the notification. By examining the list of notification codes, youÆll immediately recognize when Delphi might send a notification to the object:
TFileNotification = (fnFileOpening, fnFileOpened, fnFileClosing, fnProjectOpening, fnProjectOpened, fnProjectClosing, fnAddedToProject, fnRemovedFromProject, fnDefaultDesktopLoad, fnDefaultDesktopSave, fnProjectDesktopLoad, fnprojectDesktopSave);When you compile the project, Delphi will call the EventNotification method twice, once before the compilation and once when itÆs done, as indicated by the TEventNotification enumeration type:
TEventNotification = (enBeforeCompile, enAfterCompile);Using the first of these methods, weÆll improve our project view a little, and build the capabilities into our next example, named VcsPrj2. First, we want to add an ImageList component to the form to display icons that indicate the status of the project files. In particular, we want to indicate whether a file is open or closed. After preparing some bitmaps, weÆve assigned them using the ImageList component editor. The next step is to link the images in the ImageList component to the TreeView componentÆs StateImages property. WeÆve defined the following constants to make it easier to associate various states with the corresponding image in the list:
const stOpen = 1; stClosed = 2; stNode = 4;These constants are part of the form unitÆs interface, so weÆll be able to use them in other units of the program.
Using these constants and the methods weÆve discussed so far, we can now rewrite the formÆs UpdateAll method, set the open or closed images for the units and forms, and then display the node image for the first level nodes:
procedure TPrjInfoForm.UpdateTree;
var
I, nTot: Integer;
ChildNode: TTreeNode;
FileName: string;
begin
if ToolServices.GetProjectName = '' then
Caption := 'Project VCS'
else
begin
Caption := 'Project VCS - ' +
ExtractFileName (ToolServices.GetProjectName);
with TreeView1.Items do
begin
Clear;
BeginUpdate;
// add units
UnitsNode := AddChild (nil, 'Units');
UnitsNode.StateIndex := stNode;
nTot := ToolServices.GetUnitCount;
for I := 0 to nTot - 1 do
begin
FileName := ToolServices.GetUnitName (I);
ChildNode := AddChild (UnitsNode, FileName);
if ToolServices.IsFileOpen (FileName) then
ChildNode.StateIndex := stOpen
else
ChildNode.StateIndex := stClosed;
end;
// add forms
FormsNode := AddChild (nil, 'Forms');
FormsNode.StateIndex := stNode;
nTot := ToolServices.GetFormCount;
for I := 0 to nTot - 1 do
begin
FileName := ToolServices.GetFormName (I);
ChildNode := AddChild (FormsNode, FileName);
if ToolServices.IsFileOpen (FileName) then
ChildNode.StateIndex := stOpen
else
ChildNode.StateIndex := stClosed;
end;
EndUpdate;
end;
TreeView1.FullExpand;
end;
end;
Instead of calling this method whenever the project changes (which is fairly often), we want Delphi to do so only when we need to update the projectÆs status. To accomplish this we must declare a new add-in notification class (and a corresponding global variable):
type
TDDHPrjNotifier = class(TIAddInNotifier)
public
procedure FileNotification(NotifyCode: TFileNotification;
const FileName: string; var Cancel: Boolean); override;
procedure EventNotification(NotifyCode: TEventNotification;
var Cancel: Boolean); override;
end;
var
PrjNotif: TDDHPrjNotifier;
As you might guess, when Delphi creates and installs a version control system DLL, it then also creates and installs the PrjNotif object. The two new statements appear in the middle of the function:
function VCSInit (VCSInterface: TIToolServices): TIVCSClient; stdcall;
begin
Result := nil;
try
ToolServices := VCSInterface;
Application.Handle := ToolServices.GetParentHandle;
PrjNotif := TDDHPrjNotifier.Create;
ToolServices.AddNotifier (PrjNotif);
PrjInfoForm := TPrjInfoForm.Create (Application);
Result := TDdhProjectVcs.Create;
except
ToolServices.RaiseException(ReleaseException);
end;
end;
Delphi later removes and destroys the form and the notification object along with the VCS object:
destructor TDdhProjectVcsTDDHDemoVCS.Destroy; begin PrjInfoForm.Free; ToolServices.RemoveNotifier (PrjNotif); PrjNotif.Free; end;The most interesting part of this class is the method that responds to notification commands, the FileNotification method:
procedure TDDHPrjNotifier.FileNotification (
NotifyCode: TFileNotification;
const FileName: string; var Cancel: Boolean);
var
Node: TTreeNode;
begin
try
case NotifyCode of
fnFileOpened:
begin
// set the proper icon
Node := PrjInfoForm.FindNode (FileName);
if Node <> nil then
Node.StateIndex := stOpen;
end;
fnFileClosing:
begin
// set the proper icon
Node := PrjInfoForm.FindNode (FileName);
if Node <> nil then
Node.StateIndex := stClosed;
end;
fnProjectOpened:
PrjInfoForm.UpdateTree;
fnProjectClosing:
begin
// empty and repaint the tree
PrjInfoForm.TreeView1.Items.Clear;
PrjInfoForm.TreeView1.Repaint;
end;
fnAddedToProject:
PrjInfoForm.UpdateTree;
fnRemovedFromProject:
PrjInfoForm.UpdateTree;
end;
except
ToolServices.RaiseException(ReleaseException);
end;
end;
The two events we handle in a specific way are opening and closing files. However, itÆs important for us to see if the node is currently in the TreeView, since the user might be opening or closing a file unrelated to the project.
We accomplish this by calling the FindNode function we added to the form class. This function simply scans the TreeView component for the requested item:
function TPrjInfoForm.FindNode (Text: string): TTreeNode;
var
I: Integer;
begin
Result := nil;
for I := 0 to TreeView1.Items.Count - 1 do
if TreeView1.Items [I].Text = Text then
begin
Result := TreeView1.Items [I];
Exit;
end;
end;
To make this form work well as a VCS wizard, weÆve made one more change: When the user selects a file, we confirm that it exists (on disk) before we try to activate it.
- If the user selects a DPR file, the corresponding project is reopened, not simple redisplayed in the current editor window.
If the file doesnÆt exist, we display an error message prompting the user to create the new files, instead of the standard Delphi dialog box. (In Delphi 2, we simply display an error message.) Here is the code:
procedure TPrjInfoForm.TreeView1DblClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
if (TreeView1.Selected.Level = 1) and (
(TreeView1.Selected.Parent.Text = 'Units') or
(TreeView1.Selected.Parent.Text = 'Forms')) then
begin
if FileExists (TreeView1.Selected.Text) then
ToolServices.OpenFile (TreeView1.Selected.Text)
else
MessageDlg ('The physical file still doesn''t exist',
mtError, [mbOK], 0);
end;
end;
The effect of this code is that our demo version control system now displays different bitmaps to show the user if a file is open or closed. You can see an example of the output in Figure 15.5.
Figure 15.5: The form of the VcsDemo2 example shows bitmaps to indicate the status of the various files, and keeps track of the operations of the user.

YouÆll notice that in this example you can simply double-click on a closed file (or close one that is open) to see its icon change, without having to refresh the whole tree. However, if you save a file with a new name, youÆll have to close and reopen the window to refresh the status of the project, something weÆll fix in the next (and last) version of the program.
Module Interfaces and Module Notifications
The file notifications we handled in the last example refer to the files of a project. Unfortunately, Delphi doesnÆt notify us for each and every action that takes place. For example, we donÆt know when the user has modified or saved a file. As you can imagine, this is something that might be helpful if you build a robust and powerful version control system, or if you create advanced Delphi wizards.
The ToolServices global object defines a couple of methods we havenÆt used yet: GetModuleInterface and GetFormModuleInterface. These two functions accept a filename parameter and return a TIModuleInterface object. This class is the interface to the Delphi editor and the form designer.
In the EditIntf unit of the ToolsAPI, you can find the following declaration of the TIModuleInterface class:
type
TIModuleInterface = class(TInterface)
public
function GetEditorInterface: TIEditorInterface; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function GetFormInterface: TIFormInterface; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function GetAncestorModule: TIModuleInterface; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function GetProjectResource: TIResourceFile; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function IsProjectModule: Boolean; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function Close: Boolean; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function Save(ForceSave: Boolean): Boolean; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function Rename(const NewName: string): Boolean; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function GetFileSystem(var FileSystem: string): Boolean;
virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function SetFileSystem(const FileSystem: string): Boolean;
virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function ShowSource: Boolean; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function ShowForm: Boolean; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function AddNotifier(AModuleNotifier: TIModuleNotifier):
Boolean; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function RemoveNotifier(AModuleNotifier: TIModuleNotifier):
Boolean; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
end;
You can find a complete description of each of these methods in the source code itself. In brief, the most useful functions give you the ability to interact with several elements of the IDE. For instance, you can access the edit buffer (GetEditorInterface), and then manipulate its contents. You can access the form designer (GetFormInterface), and then manipulate the form or its components and their properties. You can access the projectÆs resource file (GetProjectResource), and then perform some action such as closing, saving, renaming, or displaying the file.
In each case above, the methods return an interface, which may return further interfaces such as a TIEditWriter (used to modify a source code file) or TIComponentInterface object. You can use the latter interface to interact with an existing component, examine its list of its properties and their values, and even change the property values by name.
Using the last two methods of the TIModuleInterface class, you can also install a specific notifier for the module. The TIModuleNotify interface declares a Notify method you should override, as well as a ComponentRenamed method. Here is a list of the notifications:
TNotifyCode = (ncModuleDeleted, ncModuleRenamed, ncEditorModified, ncFormModified, ncEditorSelected, ncFormSelected, ncBeforeSave, ncAfterSave, ncFormSaving, ncProjResModified);
Unfortunately, using these capabilities to their full extent would require very complex examples. (However, if youÆre interested in pursuing these topics, the Project Explorer demo wizard included in Delphi uses many of these techniques.)
Saving Author Information
WeÆve decided to improve our VCS demo only slightly, but (we hope) enough to give you an idea of what you can do in a VCS. Our aim is to use the source code files to store some of the version control information. Our technique wonÆt prevent programmers from editing this data, but it will demonstrate how closely an add-in tool can be integrated with Delphi. Along the way, weÆll address a bug in the previous example that relates to the Save As operation.
To respond to file save notifications, we basically need to create a distinct module notifier object for every file the user opens. This is an important thing to understand, since the module notifications donÆt pass the associated filename as a parameter. Therefore, weÆll need to store this information in each notifier object.
In addition, we need to install the module notifier into a module interface, and keep the interface object alive as long as the notifier object is active. More important, we need to destroy the module interface object when Delphi destroys the notifier.
To deal with these two issues, we can write a module notifier class that includes the filename of the current object and the module interface:
type
TDDHModNotif = class (TIModuleNotifier)
private
FileName: string;
ModIntf: TIModuleInterface;
public
constructor Create (FileN: string;
ModInterface: TIModuleInterface);
destructor Destroy; override;
procedure Notify(NotifyCode: TNotifyCode); override;
procedure ComponentRenamed(ComponentHandle: Pointer;
const OldName, NewName: string); override;
end;
Before we examine the code of this function, we should discuss how the VCS manages these objects.
In fact, we need to make several changes to the VCS class in order to add a new menu item (to let the user choose whether to save the VCS data in the source code files). This VCS adds a couple of new fields and methods:
type
TDdhProjectVcs = class (TIVCSClient)
private
// store the name in each file?
StoreAuthor: Boolean;
// list of installed module notifiers:
NotifList: TStrings;
public
constructor Create;
function GetIDString: string; override;
procedure ExecuteVerb(Index: Integer); override;
function GetMenuName: string; override;
function GetVerb(Index: Integer): string; override;
function GetVerbCount: Integer; override;
function GetVerbState(Index: Integer): Word; override;
procedure ProjectChange; override;
destructor Destroy; override;
// custom methods used to add/remove a module notifier
procedure InstallNotifier (FileName: string);
procedure RemoveNotifier (FileName: string);
end;
As you would expect, the constructor initializes the new fields, and the destructor deletes the notifier list after confirming that itÆs empty (that is, after each module notifier has been deleted):
constructor TDdhProjectVcs.Create;
begin
inherited Create;
// default: don't store the name
StoreAuthor := False;
// create the list
NotifList := TStringList.Create;
end;
destructor TDdhProjectVcs.Destroy;
begin
try
// destroy form and global notifier
PrjInfoForm.Free;
ToolServices.RemoveNotifier (PrjNotif);
PrjNotif.Free;
// check if the list is empty (it should
// always be, at this time) and remove it
if NotifList.Count > 0 then
ShowMessage (Format (
'Error: %d module notifiers have not been removed',
[NotifList.Count]));
NotifList.Free;
except
ToolServices.RaiseException(ReleaseException);
end;
end;
If everything works correctly, you should never see the destructorÆs error message. However, in case of an error some notifier objects might remain in memory when the destructor is called, and we prefer to leave this debug check in the code as a sort of warning tool. Failing to destroy a notifier causes a memory leak inside Delphi, but it shouldnÆt cause any other side effects.
The NotifList object manages notifiers using two methods, InstallNotifier and RemoveNotifier. To install a notifier, the program retrieves a module interface for the file, creates the notifier object (using the module interface filename and the module interface object as parameters), adds the notifier to the module interface, and then adds the object and the filename to the list:
procedure TDdhProjectVcs.InstallNotifier (FileName: string);
var
ModIntf: TIModuleInterface;
Notif: TDDHModNotif;
begin
// get the module interface
ModIntf := ToolServices.GetModuleInterface (FileName);
if ModIntf <> nil then
begin
// create the module notifier
Notif := TDDHModNotif.Create (FileName, ModIntf);
// install the notifier
ModIntf.AddNotifier (Notif);
// add the notifier to the list
NotifList.AddObject (FileName, Notif);
end;
end;
procedure TDdhProjectVcs.RemoveNotifier (FileName: string);
var
ItemNo: Integer;
begin
// checks if the notifier is in the list
ItemNo := NotifList.IndexOf (FileName);
if ItemNo >= 0 then
begin
// destroy the notifier
TDDHModNotif (NotifList.Objects [ItemNo]).Free;
// remove the corresponding list item
NotifList.Delete (ItemNo);
end;
end;
YouÆll notice that the method above removes the notifier but doesnÆt uninstall it. This is OK because the module notifierÆs destructor eliminates its connection to the module interface, and then releases the module interface as well. WeÆll see this code later on.
Now letÆs consider some of the changes to the VCS object that relate to the menu items. Here are the updated versions of the four verb methods that relate to counting, showing, and executing the code for the VCS menu items. These methods should be easy to understand without extensive discussion:
function TDdhProjectVcs.GetVerbCount: Integer;
begin
Result := 4;
end;
function TDdhProjectVcs.GetVerb(Index: Integer): string;
begin
case Index of
0: Result := '&Project Information...';
1: Result := '&Store Author on Save';
2: Result := ''; // separator
3: Result := '&About DDH Project VCS...';
end;
end;
procedure TDdhProjectVcs.ExecuteVerb(Index: Integer);
begin
case Index of
0: try
PrjInfoForm.UpdateTree;
PrjInfoForm.Show;
except
ToolServices.RaiseException(ReleaseException);
end;
1: // toggle the flag
StoreAuthor := not StoreAuthor;
3: // about box
MessageDlg ('DDH Project Version Control System'#13#13 +
'From the "Delphi Developer''s Handbook"'#13 +
'by Marco Cantù and Tim Gooch',
mtInformation, [mbOK], 0);
end;
end;
function TDdhProjectVcs.GetVerbState(Index: Integer): Word;
begin
Result := vsEnabled; // default
try
case Index of
0: // disable first item if no project is active
if ToolServices.GetProjectName = '' then
Result := 0;
1: // check the second item when appropriate
if StoreAuthor then
Result := vsEnabled + vsChecked;
//3: always enabled: nothing to do
end;
except
ToolServices.RaiseException(ReleaseException);
end;
end;
In the GetVerbState method, notice how we handle the check mark for the Store Author menu item. As we mentioned before, the vsEnabled and vsChecked identifiers are integer constantsùnot enumerated values.
We had to make another set of changes in the TDDHPrjNotifier classÆs FileNotification method, because this class creates and removes the module notifiers when the user opens or closes a file. In reality, for the fnFileOpened notification weÆve added just few lines of code to register a notifier only if the file is a Pascal source file (that it, if it has a .pas extension). In addition, weÆll create the notifier when the user adds a new unit to the project. Here is the new code (not the complete listing) for these two branches of the FileNotification methodÆs case statement:
fnFileOpened:
if ExtractFileExt (FileName) = '.pas' then
DdhPrjVcs.InstallNotifier (FileName);
fnAddedToProject:
if ExtractFileExt (FileName) = '.pas' then
DdhPrjVcs.InstallNotifier (FileName);
Of course, weÆll remove the notifier when the user closes the file. The RemoveNotifier method checks whether the corresponding notifier actually existed:
fnFileClosing:
if ExtractFileExt (FileName) = '.pas' then
DdhPrjVcs.RemoveNotifier (FileName)
fnRemovedFromProject:
if ExtractFileExt (FileName) = '.pas' then
DdhPrjVcs.RemoveNotifier (FileName);
Now that we know how the rest of the program (the VCS object and the project notifier) interacts with the module notifier class, we can finally examine its methods. The constructor of the module notifier class is quite simple, since it simply stores its parameters:
constructor TDDHModNotif.Create (FileN: string; ModInterface: TIModuleInterface); begin inherited Create; // store the parameters FileName := FileN; ModIntf := ModInterface; Modified := False; end;The destructor simply disconnects the notifier from the module interface, and then releases the module interface object:
destructor TDDHModNotif.Destroy; begin // remove the module notifier ModIntf.RemoveNotifier (self); // release the interface ModIntf.Release; inherited Destroy; end;If you like, you can add a call to Beep (or SysUtils.Beep) inside this method to confirm that Delphi actually executes this code.
Of course, this classÆs key method is Notify. As weÆve already mentioned, this method receives only a notification code, but we know which file and module interface object the notification object refers to because weÆve stored them inside the object.
Since the code for this method is quite complex, weÆve divided it into smaller and more understandable pieces (dividing the local variable declarations, as well). The simplest code responds to the ncEditorModified notification:
procedure TDDHModNotif.Notify (NotifyCode: TNotifyCode);
begin
case NotifyCode of
ncEditorModified:
// set the modified flag
Modified := True;
By setting this flag, we avoid adding user information to a file when the user saves it without making any changes. This is one of the checks we do when the ncBeforeSave notification arrives:
var
WriIntf: TIEditWriter;
ReadIntf: TIEditReader;
EditIntf: TIEditorInterface;
FirstLine, UserName, NewFirstLine: string;
NameSize, FirstLineLen: Integer;
begin
...
ncBeforeSave:
// if the file has changed
// and the StoreAuthor flag is set
if Modified and DdhPrjVcs.StoreAuthor then
begin
// get the module editor interface
EditIntf := ModIntf.GetEditorInterface;
if EditIntf <> nil then
try
// create a reader object
ReadIntf := EditIntf.CreateReader;
if ReadIntf <> nil then
try
SetLength (FirstLine, 100);
ReadIntf.GetText (0, PChar(FirstLine),
Length (FirstLine));
finally
// release the interface
ReadIntf.Release;
end;
// define the output string
// with user name, date, and time
NameSize := 100;
SetLength (UserName, 100);
GetUserName (PChar (UserName), NameSize);
UserName := PChar (UserName); // length fix
NewFirstLine := '// Updated by ' + UserName +
', ' + DateTimeToStr (Now) + #13;
WriIntf := EditIntf.CreateWriter;
if WriIntf <> nil then
try
// check if user and day have not changed
if StrLComp (PChar(FirstLine),
PChar(NewFirstLine), NameSize + 22) = 0 then
begin
// get the length of the first line
FirstLineLen := Pos (#13, FirstLine) + 1;
// remove the current first line
WriIntf.DeleteTo (FirstLineLen);
end;
// insert the new string
WriIntf.Insert (PChar (NewFirstLine));
// release the interface
WriIntf.Release;
// reset the modified flag
Modified := False;
finally
// release the interface
WriIntf.Release;
end;
finally
// release the interface
EditIntf.Release;
end;
end;
The core of this method is at the point where we create the reader and then the writer object by calling the editor interfaceÆs CreateReader and CreateWriter methods (we obtain the editor interface from the module interface). Once this is done, you can either access the current text or insert new text. These are the definitions of the reader and the writer interfaces:
type
TIEditReader = class(TInterface)
public
function GetText(Position: Longint; Buffer: PChar;
Count: Longint): Longint; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
end;
TIEditWriter = class(TInterface)
public
function CopyTo(Pos: Longint): Boolean; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function DeleteTo(Pos: Longint): Boolean; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function Insert(Text: PChar): Boolean; virtual;
stdcall; abstract;
function Position: Longint; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
function GetCurrentPos: TCharPos; virtual; stdcall; abstract;
property CurrentPos: TCharPos read GetCurrentPos;
end;
- To change the current position within a file (before writing to it), youÆll need to use the TIEditView interface. Fortunately, we donÆt need this capability in our example (it would add a considerable amount of complexity).
However, before writing the text our VCS determines whether the first part of the string (holding the user name and the date) has changed. If it hasnÆt changed, we remove the first line before inserting the new one, to avoid an output like the following:
// Updated by Marco, 11/11/97 5:52:54 PM // Updated by Marco, 11/11/97 5:55:54 PM // Updated by Marco, 11/11/97 5:58:54 PM
In other words, if the same user saves a file twice in a day, weÆll record only the last operation. Of course, this is just a matter of how we wrote this program: since you have the source code, you can easily modify this rule to work the way you prefer.
As weÆve stated before, you need to remember to release all the interfaces you allocate. When you do this, itÆs important to call Release and not Free because (in theory) itÆs possible for two interface objects to refer to the same element. If you call Release, it reduces the reference count, and frees the object only when the reference count reaches zero. ItÆs also better to release the interfaces inside a finally block, to avoid a memory leak should an exception occur.
The rest of the module notifierÆs Notify method is much simpler. When the user renames a module (by selecting the Save As menu command), we must first to update the project view. Not handling the effect of renaming a unit was actually a bug of the previous versions of our VCS. The strange thing is that even if you handle Delphi project notifications, Delphi will completely ignore the Save As operation. This is only a file-level notification, not a project-level one.
Once weÆve refreshed the project view, we remove the current notifier (which now refers to a file that doesnÆt exist any more) and install a new notifier for the new file. However, since we donÆt know the new name of the file, the only technique weÆve found is to scan all the project files and install a notifier for each Pascal file that doesnÆt already have one:
var
FileN: string;
I: Integer;
begin
...
ncModuleRenamed:
begin
// update the project view
PrjInfoForm.UpdateTree;
// remove the notifier for the old file
DemoVCS.RemoveNotifier (FileName);
// looks for the new file name
// and installs a new notifier for it
begin
FileN := ToolServices.GetUnitName (I);
if (ToolServices.IsFileOpen (FileN)) and
(ExtractFileExt (FileName) = '.pas') and
(DemoVCS.NotifList.IndexOf (FileN) < 0) then
DemoVCS.InstallNotifier (FileN);
end;
end;
The last branch of the Notify methodÆs case statement handles the module removal:
ncModuleDeleted:
// unregister and remove the notifier
DemoVCS.RemoveNotifier (FileName);
YouÆll recall that we also declared an implementation of the ComponentRenamed method in the notifier object class. We donÆt really need to implement this method, but we decided to do so anyway (just in case Delphi calls it). This is just a do-nothing method:
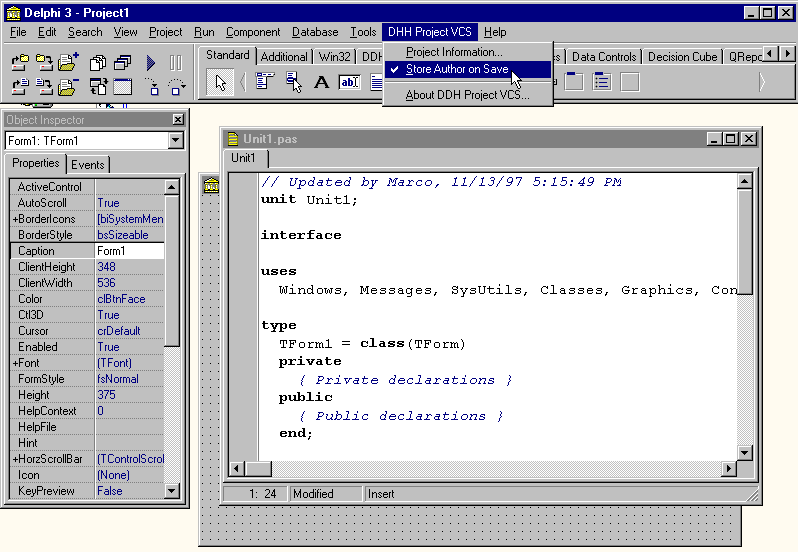
procedure TDDHModNotif.ComponentRenamed( ComponentHandle: Pointer; const OldName, NewName: string); begin // do nothing end;As a result of all this effort, the Store Author option of the VCS system (something you might turn on by default in the VCS constructor) adds the authorÆs name to each source file (along with the date and time) whenever the user modifies or saves the file. You can see the result of this option in Figure 15.6. Of course, a real VCS system should also store the changes to the file and not just the fact that something has changed. However, this example was meant to illustrate some integration techniques, and not to build a professional version control tool.
Figure 15.6: The new menu item of the Demo VCS, and its effect: adding author and time of each edit to a file in the source code itself.