Managing Your Web Server
Your servers present your company to the world on the Internet
and are an integral part of internal operations.
To ensure continuous, secure, and efficient operation,
Internet Connection Secure Server provides facilities for monitoring and managing your server.
This chapter describes how to manage and monitor
your servers and includes the following topics:
A network management system is a program
that runs continuously and is used to monitor,
reflect status of, and control a network.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), a popular protocol
for communicating with devices in a network,
is the current network management standard.
The network devices typically have an SNMP agent
and one or more subagents.
The SNMP agent talks to the network management station
or responds to command line SNMP requests.
The SNMP subagent retrieves and updates data and gives
that data to the SNMP agent to communicate back to the requester.
The Internet Connection Secure Server provides an SNMP management information base
(MIB) and SNMP subagent
so you can use any network management system,
such as IBM NetView for AIX, TME10 Distributed Monitoring,
or HP OpenView,
to monitor your server's health, throughput, and activity.
The MIB data describes the Web server being managed,
reflects current and recent server status,
and provides server performance data.
The network management system uses SNMP GET commands
to look at MIB values on other machines.
It then can notify you if specified threshold values are exceeded.
You can affect server performance, by modifying configuration
data for a server, to proactively tune or fix server problems
before they become server outages.
The system usually provides an SNMP agent
for each network management station.
The user or a programmer sends a GET command to the SNMP agent.
In turn, this SNMP agent sends a GET command to retrieve
the specified MIB variable values from a subagent responsible
for those MIB variables.
The Internet Connection Secure Server provides a subagent that updates and retrieves MIB data.
The subagent responds with the appropriate MIB data
when the SNMP agent sends a GET command.
The SNMP agent communicates the data to the network management station.
The network management station can notify you
if specified threshold values are exceeded.
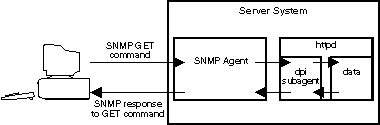
The Internet Connection Secure Server SNMP support includes an SNMP subagent that uses
Distributed Protocol Interface (DPI) capability.
DPI is an interface between an SNMP agent and its subagents.
The Internet Connection Secure Server MIB is modeled after the HTTP MIB proposal.
MIB layout includes Variable Name, Object ID, Type, and Description.
The following Variable Names and Object IDs
are provided for SNMP support with the Internet Connection Secure Server:
- EntityDescription
-
- Description
- Identifies a server in human-readable form.
This read-only value is not customizable.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.1.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- An appropriate value for your server installation and platform.
- EntityObjectID
-
- Description
- Identifies a particular server in machine-readable
form, providing a globally unique name among other applications
and versions.
This read-only value is not customizable.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.2.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.10.1
- EntityContact
-
- Description
-
Indicates who to contact if a problem or question
about this running server arises.
It is human-readable and frequently contains the e-mail address
of the on-site system administrator responsible for server maintenance.
The value for EntityContact may be customized with the
WebMasterEmail directive in the httpd.conf file.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.3.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- webmaster
- EntityProtocol
-
- Description
-
Identifies the exact protocol and its version that
a particular server supports.
For a Web server, the protocol is HTTP.
This read-only identifier is in machine-readable form
and is not customizable.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.4.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.12.1
- EntityProtocolVersion
-
-
- Description
-
This human-readable string identifies the protocol this server
supports and the protocol version.
Similar to EntityProtocol.
This read-only value is not customizable.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.5.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- HTTP/1.1
- EntityName
-
- Description
-
This human-readable string provides the name of the host this
Web server runs on.
The value for EntityName may be customized with the
HostName directive in the httpd.conf file.
It is read-only and set by system-specific code
at server initialization time.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.6.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- www.raleigh.ibm.com
- EntityAddress
-
- Description
-
This human-readable string provides the IP address of the host
this Web server runs on.
It is read-only and set by system-specific code
at server initialization time.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.7.1
- Type
- IpAddress
- Default value
- 0.0.0.0
- EntityPort
-
- Description
-
This human-readable string provides the port number this
Web server listens to.
It is read-only and set by system-specific code
at server initialization time.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.8.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- EntityType
-
- Description
-
This machine-readable integer differentiates between
several server roles.
Possible values are:
- 1
- Simple or normal HTTP server
- 2
- Proxy server
- 3
- Caching server
It is read-only and set by system-specific code
at server initialization time.
The information is taken from the httpd configuration file.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.9.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 1
- CurrentThreads
-
- Description
-
Indicates how many threads the server has currently.
The total number of active threads is the sum of the MIB values,
applInboundAssociations and applOutboundAssociations.
This information is read-only.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.10.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- MaxThreads
-
- Description
-
Indicates the maximum number of threads the server can have.
To affect server performance,
use the MaxActiveThreads directive to modify
the value for MaxThreads in the httpd.conf file.
This is read-only information.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.11.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- MinThreads
-
- Description
-
Indicates the minimum number of threads the server can have.
This is read only information.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.1.1.1.12.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 1
- SummaryRequests
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of request the server received
plus the total number of requests the server generated
(for example, as a proxy server).
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.1.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- SummaryRequestErrors
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of request errors detected by the server.
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.2.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- SummaryRequestDiscards
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of requests discarded by the server
(for any reason).
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.3.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- SummaryResponses
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of responses generated or
received by this server.
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.4.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- SummaryResponseDiscards
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of responses discarded by the server.
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.5.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- SummaryInUnknowns
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of unknown messages received
by this server.
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.6.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- SummaryInBytes
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of bytes received by this server.
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.7.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- SummaryOutBytes
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of bytes sent out by this server.
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.1.1.8.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- TotalTimeouts
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of timeouts on the Web server.
This read-only information is updated as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.4.0
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 0
- LastTimeoutEntityIndex
-
- Description
-
This value is for future extensibility and provides support
for the Application Table.
This read-only value is always 1 and is not customizable.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.5.0
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 1
- LastTimeoutRemoteAddress
-
- Description
-
Provides the IP address of the machine that timed out last.
This read-only value is updated by server code as the server runs.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.120.1.1.2.6.0
- Type
- IpAddress
- Default value
- 0.0.0.0
- applName
-
- Description
-
The name that the network service application is known by.
This read-only value is not customizable.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.2.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- Internet Connection Server platform
- applDirectoryName
-
- Description
-
The X.500 name for Web server.
This read-only value is not customizable
and is currently not supported by Internet Connection Secure Server Web server.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.3.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- Not available
- applVersion
-
- Description
-
The version of software the server is running.
This human-readable value is read-only and not customizable.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.4.1
- Type
- OCTET_STRING
- Default value
- 4.2
- applUptime
-
- Description
-
This value is how long the server has been up.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.5.1
- Type
- TimeTicks
- Default value
- 0
- applOperStatus
-
- Description
-
Indicates the operational status of the Web server.
The Internet Connection Secure Server sets this value to up at server startup.
It is currently a read-only value.
Additional standardized values for this MIB variable
include down, halted, congested, and restarting.
These values may be used in the future.
Standardized values include:
- 1
- Up - indicates that the server is operational and available.
- 2
- Down - indicates that the Web server is not available.
- 3
- Halted - indicates that the Web server is operational but
not available.
- 4
- Congested - indicates that the server is operational but
no additional inbound associations can be accommodated.
- 5
- Restarting - indicates that the server is currently
unavailable but is in the process of restarting and will be
available soon.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.6.1
- Type
- INTEGER
- Default value
- 1
- applLastChange
-
- Description
-
Indicates how long from when the server came up (applUptime)
that the applOperStatus changed.
Currently this will always be 0 because applOperStatus
is only set to up at server startup.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.7.1
- Type
- TimeTicks
- Default value
- 0
- applInboundAssociations
-
- Description
-
Indicates the number of inbound connections currently running
or how many threads are processing received requests.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.8.1
- Type
- Gauge32
- Default value
- 0
- applOutboundAssociations
-
- Description
-
Indicates the number of outbound connections that the server
is currently handling
or how many threads are processing outbound requests.
This value is 0 if the server is not acting as a proxy server.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.9.1
- Type
- Gauge32
- Default value
- 0
- applAccumulatedInboundAssociations
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of server's inbound connections
until this time.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.10.1
- Type
- Gauge32
- Default value
- 0
- applAccumulatedOutboundAssociations
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of server's outbound connections
until this time.
This value is 0 if the server is not acting as a proxy server.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.11.1
- Type
- Counter32
- Default value
- 0
- applLastInboundActivity
-
- Description
-
Indicates the time since applUptime that
the last inbound connection was made.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.12.1
- Type
- TimeTicks
- Default value
- 0
- applLastOutboundActivity
-
- Description
-
Indicates the time since applUptime that
the last outbound connection was made.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.13.1
- Type
- TimeTicks
- Default value
- 0
- applRejectedInboundAssociations
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of requests the server has rejected.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.14.1
- Type
- Counter32
- Default value
- 0
- applFailedOutboundAssociations
-
- Description
-
Indicates the total number of the server's outbound requests
that failed.
This is a read-only value.
- Object ID
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27.1.1.15.1
- Type
- Counter32
- Default value
- 0
Note: The timestamp values for the Internet Connection Secure Server MIB variables,
applLastChange, applLastInboundActivity, and applLastOutboundActivity,
vary from RFC 1565.
In RCF 1565, timestamps are relative to sysUpTime.
These three Internet Connection Secure Server timestamp values are relative to applUptime.
The Internet Connection Secure Server provides a default e-mail address, webmaster,
for the Web server administrator to receive problem reports from SNMP.
Use the WebMasterEmail directive to customize the mail address.
The typical format for this value is user@rootname.
For more information about the WebMasterEmail directive,
see "WebMasterEmail - Creating an e-mail address to receive SNMP problem reports".
To get a DPI-capable SNMP agent for Windows NT, install the
SystemView Agent Developers
Toolkit for Windows NT, which can be downloaded
from the http://www.software.ibm.com/download/ URL.
Before you start the SystemView
snmpd process, you must
disable the Microsoft Windows NT SNMP support.
The snmpd supports DPI subagents and
Microsoft-compliant agents.
To disable the Microsoft Windows NT SNMP support:
- From your Windows NT version 4.0 desktop,
click on the My Computer icon.
From your Windows NT version 3.51 desktop,
click on the Main icon.
- Click on the Control Panel icon.
- Click on the Service icon.
- Select SNMP.
-
For Windows NT version 4.0, click HW Profiles.
For Windows NT version 3.51, click Startup.
- For Windows NT version 4.0, click Disable.
For Windows NT version 3.51, under Startup Type,
click Disable.
Note:
If you do not disable the Microsoft Windows NT SNMP support,
the Internet Connection Secure Server SNMP subagent will not be able to connect
to the snmpd agent.
To configure the SystemView
SNMP agent, follow the instructions
in "Providing a security password for SNMP".
You can create community names (passwords).
The default SNMP community name is public.
Before creating passwords for server communities,
configure the SystemView SNMP agent.
- From your desktop, click on the SystemView Agent icon.
- Click on snmpcfg.
-
In the SNMP Configuration dialog box,
add the community name.
For testing purposes, enter public
as the community name.
This allows any host in any network
to access the SNMP MIB variables.
After you have verified that these values work, you can change
them according to your requirements.
-
Check the sva.batch file and
ensure that the -dpi option is specified
before starting snmpd.
Use the SNMPCommunityName directive to define the password
used between the Internet Connection Secure Server DPI subagent and the SNMP agent.
The default is public.
If you change this value, you must also add the new community name
to the SystemView Agent
snmpcfg.
For more information about the SNMPCommunityName directive,
see "SNMPCommunityName - Providing a security password for SNMP".
Use the SNMP directive to enable or disable SNMP support.
To enable SNMP support, change the SNMP value to on.
The default SNMP value is off.
For more information about the SNMP directive,
see "Turning the SNMP support on and off from the whttpg command".
Use these flags to turn the SNMP support in the Internet Connection Secure Server on and off.
The -snmp flag turns the SNMP support on.
The -nosnmp flag turns the SNMP support off.
This overrides what is defined in the httpd.conf file.
For more information about the whttpg command, see "whttpg command".
The Internet Connection Server Activity Monitor allows you to display server and network
performance and status statistics, and access log entries,
without being on the same machine that is running the server.
This option provides significantly more information
than opening the console window.
In addition, you can use the Performance Monitor built into Windows
NT to monitor your server.
You do not need to enable or configure the Server Activity Monitor function.
By default, the Server Activity Monitor is enabled by the following Service directive
in the configuration file:
Service /Usage* INTERNAL:UsageFn
To view server statistics,
network statistics, and access log entries, use either of the
following methods:
-
Use any browser and specify URL
http://your.server.name/Usage/Initial,
where your.server.name is the fully qualified
name of your host, for example, www.ibm.com.
-
Click Configuration and Administration Forms on the
server Front page.
Then click
Server Activity Monitor in the
System Management section.
The following sections describe the type of information that is
available and provide
hints and tips on monitoring certain statistics.
To update the
statistics on a page, click Refresh.
Figure 3 shows an example of the server
statistics that are displayed on the Basic Status page.
Figure 3. Example of Basic Status page statistics
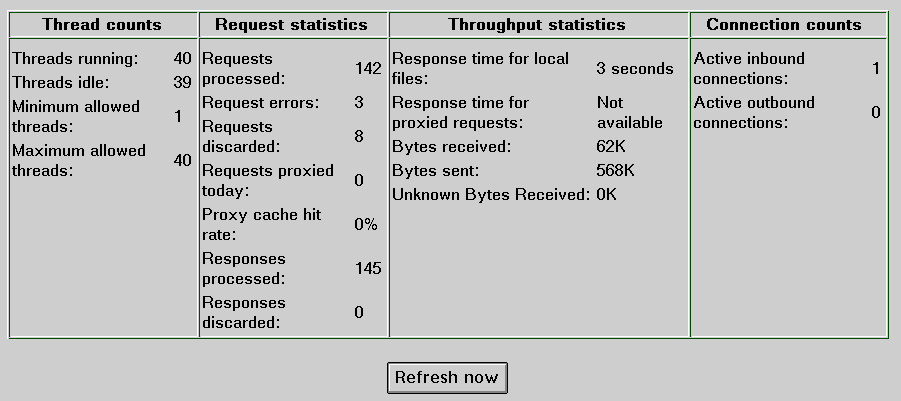
Hints and Tips:
-
If the number of idle threads is low, you may need
to increase the number of threads that are available to the server.
-
To monitor server response, use the
Response time for local files statistic.
-
To monitor traffic, use the Requests processed,
Bytes received, and Bytes sent statistics.
Figure 4 shows an example of the network
statistics that are displayed on the Network Status page.
Figure 4. Example of Network Status page statistics

Note:
Incoming and outgoing data values
include only
data received and sent by the server.
The access log page
displays the 20
most recent entries in the access log.
For more information on the access log, go to "Tailoring the logs your server keeps".
You can select the Internet Connection Secure Server
as an object for the Performance Monitor
built into Windows NT to monitor errors and performance of your server.
The HTTP port used by the server is displayed as the corresponding
instance.
These are the counters you can select to monitor:
- Counter
- Definition
- CGI requests
- The total number of CGI requests processed by the server
- Error 200 OK
- The total number of requests receiving a 200 response code.
This means success.
- Error 302
- The total number of requests receiving a 302 response code.
- Error 401
- The total number of requests receiving a 401 response code.
- Error 403
- The total number of requests receiving a 403 response code.
- Error 404
- The total number of requests receiving a 404 response code.
- Error 407
- The total number of requests receiving a 407 response code.
- Error 500
- The total number of requests receiving a 500 response code.
- Error Level 200
- The total number of requests receiving a response code in the
range 200-299.
- Error Level 300
- The total number of requests receiving a response code in the
range 300-399.
- Error Level 400
- The total number of requests receiving a response code in the
range 400-499.
- Error Level 500
- The total number of requests receiving a response code in the
range 500-599.
- GET requests
- The total number of GET requests processed by the server.
- HEAD requests
- The total number of HEAD requests processed by the server.
- POST requests
- The total number of POST requests processed by the server.
- Total ICAPI requests
- The total number of requests serviced by the IBM APIs.
- Total KBytes received
- The number of kilobytes received by the server.
- Total KBytes received /sec
- The number of kilobytes received by the server per second.
- Total KBytes sent
- The total number of kilobytes sent by the server.
- Total KBytes sent/sec
- The number of kilobytes sent by the server per second.
- Total requests
- The number of requests processed.
- Total requests/sec
- The number of requests processed per second.
Note: The server must be running so that it can be monitored by
the Performance Monitor.
If you restart the server, the monitoring will start back up
where it left off, but if the server dies, you will have to reset
the monitoring to begin again once the server is back up.
See the Microsoft Windows NT documentation for more details about
how the Performance Monitor works.
[ Top of Page | Previous Page | Next Page | Table of Contents ]
�


