



The Bezier controller is the most versatile controller in 3D Studio MAX. Bezier controllers interpolate between keys using an adjustable spline curve; they are the default controller for most parameters.
Use Bezier controllers whenever you want fully adjustable interpolation between keys. Bezier is the only controller that supports the following:
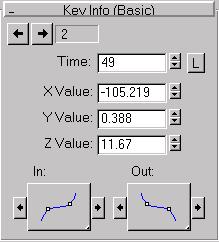
Key number: Click the right or left arrows to go to the next or previous key. The field shows the current key number.
Time: Enter a value to specify when in time the key occurs.
Time Lock: Controls the ability to drag the key horizontally in Track View edit modes.
X/Y/Z: Adjusts the position of the selected object at the current key.
Key Tangent (flyouts): Two large flyouts that set the interpolation properties of the in tangent and out tangent of the key.
Choosing Bezier Tangent Types: Set the tangent types for one or more keys in the same track using the In and Out tangent flyouts.
![]()
Smooth: Creates smooth interpolation through the key.
![]()
Linear: Creates linear interpolation at the key, like a linear controller.
A linear tangent only affects the curve near the key. Full linear interpolation between two keys only occurs when the Out tangent of the first key and the In tangent of the next key both use a linear tangent.
![]()
Step: Creates binary interpolation from one key to the next. Step tangents require a matched set between the Out tangent of one key and the In tangent of the next key.
Choosing step for the In tangent of the current key also changes the Out tangent of the previous key.
Choosing step for the Out tangent of the current key also changes the In tangent of the next key.
Using step tangents, the outgoing value of a key is held constant until the time of the next key is reached. The value then abruptly jumps to the value of the next key. Use this tangent when you want to animate On/Off switching or instantaneous changes from one value to the next.
![]()
Slow: Causes the interpolated rate of change to slow down around the key.
A slow In tangent decelerates as it approaches the key.
A slow Out tangent begins slow and accelerates as it leaves the key.
![]()
Fast: Causes the interpolated rate of change to speed up around the key. The effect is the opposite of using slow.
A fast In tangent accelerates as it approaches the key.
A fast Out tangent begins fast and decelerates as it leaves the key.
![]()
Custom: Displays adjustable tangent handles at the key in Function Curves mode. Choosing Custom for either tangent also sets the other tangent to custom.
Tangent Copy (buttons): Use the arrow buttons to either side of the Key Tangent flyouts to copy the tangent type between the tangents of the current key or between the tangents of the previous and next key.
The left arrow of the In tangent copies to the Out tangent of the previous key.
The right arrow of the In tangent copies to the Out tangent of the current key.
The left arrow of the Out tangent copies to the In tangent of the current key.
The right arrow of the Out tangent copies to the In tangent of the next key.
3Choosing Bezier Tangent Types: Set the tangent types for one or more keys in the same track using the In and Out tangent flyouts.
Bezier Scale Controller (Lock X): In the Key Info dialog for the Bezier Scale controller, a Lock button is added beside the X Scale spinner. When turned on, only the X value affects all three axes of scale. The Y and Z values are ignored and their function curves are not displayed.
![]()
When X is locked, the Y and Z values are not affected by changes in the X value. If you lock X when all three axes are at identical values, alter the X value, and then unlock X, the Y and Z values remain where they were while X retains its new value.
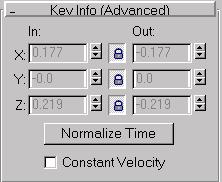
In/Out: The In field is the rate of change as the parameter approaches the key. The Out field is the rate of change as the parameter leaves the key.
These fields are only active for keys using the Custom tangent type.
The number in the field is the rate of change expressed as parameter units per Tick.
Lock button: When Lock is on, changing one Custom tangent changes the other by equal but opposite amount. For example, if the Lock button is on and the In value is 0.85, then the Out value is -0.85.
Normalize Time: Averages out the position of the keys in time. Applicable to any consecutive blocks of selected keys. Useful if you have an object that speeds up, slows, down, speeds up, slows down, and you want to smooth out the motion.
Constant Velocity: When this check box is set for a key, values in between that key and the next one are interpolated in a way that makes the object move at a constant velocity across that curve segment.
You can use the arrows in the Key Info (Basic) rollout to step through Keyframes.
The key is moved in time to average the velocity through the key.